10+ Examples Of Ionic And Covalent Bonds Practice Problems
What are ionic and covalent bonds?
Ionic and covalent bonds are the two main types of chemical bonds. Ionic bonds are formed between atoms of metals and nonmetals, while covalent bonds are formed between atoms of nonmetals.
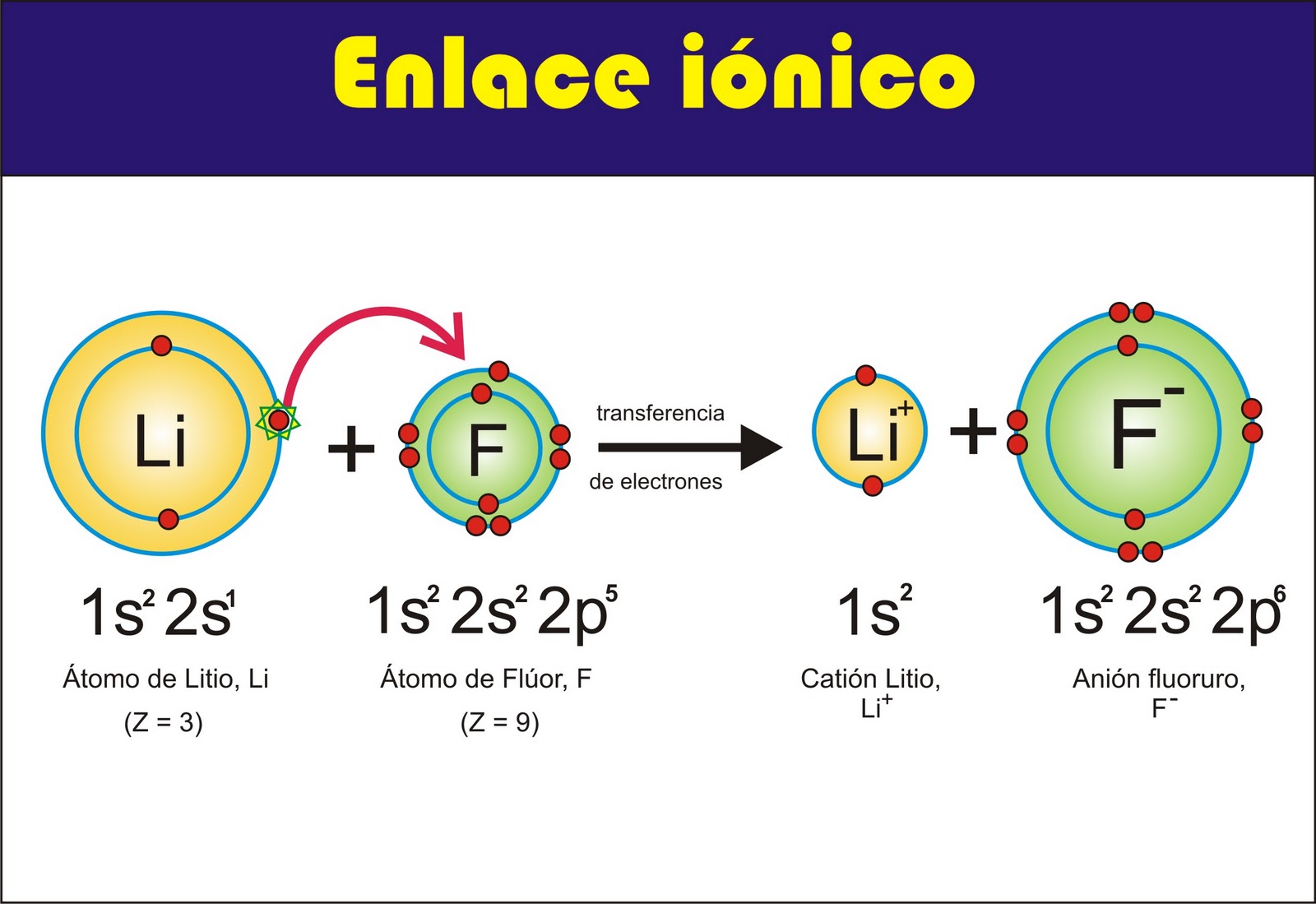
Ionic bonds are formed when one atom transfers one or more electrons to another atom. The atom that loses electrons becomes a positively charged ion, and the atom that gains electrons becomes a negatively charged ion. The oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other by electrostatic forces, forming an ionic bond.
Covalent bonds are formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. The shared electrons are attracted to the nuclei of both atoms, forming a covalent bond.
Ionic and covalent bonds are important because they determine the properties of matter. Ionic compounds are typically hard, brittle, and have high melting and boiling points. Covalent compounds are typically soft, ductile, and have low melting and boiling points.
The type of bond that is formed between two atoms depends on the electronegativity of the atoms. Electronegativity is a measure of how strongly an atom attracts electrons. The more electronegative an atom, the more strongly it attracts electrons. If the difference in electronegativity between two atoms is large, an ionic bond will form. If the difference in electronegativity is small, a covalent bond will form.
Ionic and Covalent Bonds
Ionic and covalent bonds are the two main types of chemical bonds. They are formed when atoms share or transfer electrons in order to achieve a stable electron configuration.
- Definition: Ionic bonds are formed between atoms of metals and nonmetals, while covalent bonds are formed between atoms of nonmetals.
- Electronegativity: The electronegativity of an atom determines the type of bond that will form. If the difference in electronegativity between two atoms is large, an ionic bond will form. If the difference in electronegativity is small, a covalent bond will form.
- Properties: Ionic compounds are typically hard, brittle, and have high melting and boiling points. Covalent compounds are typically soft, ductile, and have low melting and boiling points.
- Examples: Sodium chloride (NaCl) is an example of an ionic compound. Water (H2O) is an example of a covalent compound.
- Importance: Ionic and covalent bonds are important because they determine the properties of matter.
Ionic and covalent bonds are essential to our understanding of chemistry. They are the building blocks of all matter, and they determine the properties of the materials we use every day.
Definition
This definition is the foundation for understanding the concept of ionic and covalent bonds, which are the two main types of chemical bonds. By understanding the difference between these two types of bonds, we can better understand the properties of matter, the reactions that occur between atoms, and the structure of molecules.
- Facet 1: Electronegativity and Bond Type
Electronegativity is a measure of the attraction that an atom has for electrons. Metals have low electronegativity, while nonmetals have high electronegativity. When a metal and a nonmetal bond, the electrons are transferred from the metal to the nonmetal, resulting in the formation of an ionic bond. When two nonmetals bond, the electrons are shared between the two atoms, resulting in the formation of a covalent bond. - Facet 2: Properties of Ionic and Covalent Compounds
Ionic compounds are typically hard, brittle, and have high melting and boiling points. This is because the strong electrostatic forces between the positive and negative ions hold the compound together tightly. Covalent compounds are typically soft, ductile, and have low melting and boiling points. This is because the covalent bonds between the atoms are not as strong as the ionic bonds between the ions. - Facet 3: Examples of Ionic and Covalent Compounds
Examples of ionic compounds include sodium chloride (NaCl), potassium chloride (KCl), and calcium oxide (CaO). Examples of covalent compounds include water (H2O), methane (CH4), and carbon dioxide (CO2). - Facet 4: Importance of Ionic and Covalent Bonds
Ionic and covalent bonds are essential for the formation of all matter. They determine the properties of materials and the reactions that occur between atoms. Understanding the difference between these two types of bonds is essential for understanding chemistry and the world around us.
In summary, the definition of ionic and covalent bonds is the foundation for understanding the structure and properties of matter. By understanding the difference between these two types of bonds, we can better understand the world around us.
Electronegativity
Electronegativity is a fundamental property of atoms that influences the formation of chemical bonds. It is defined as the ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itself. The electronegativity of an atom is determined by its atomic number and the number of electrons in its outermost shell. Atoms with high electronegativity have a strong attraction for electrons, while atoms with low electronegativity have a weak attraction for electrons.
- Facet 1: Electronegativity and Bond Type
The electronegativity of an atom determines the type of bond that will form between two atoms. If the difference in electronegativity between two atoms is large, an ionic bond will form. This is because the atom with the higher electronegativity will attract the electrons away from the atom with the lower electronegativity, resulting in the formation of positive and negative ions. If the difference in electronegativity between two atoms is small, a covalent bond will form. This is because the electrons will be shared between the two atoms, resulting in the formation of a covalent bond. - Facet 2: Examples of Ionic and Covalent Bonds
Examples of ionic bonds include sodium chloride (NaCl) and potassium chloride (KCl). In these compounds, the metal atoms (sodium and potassium) have low electronegativity and the nonmetal atoms (chlorine) have high electronegativity. This results in the formation of ionic bonds, where the metal atoms transfer electrons to the nonmetal atoms. Examples of covalent bonds include hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2). In these compounds, the atoms have similar electronegativities and share electrons to form covalent bonds. - Facet 3: Implications for "ejemplos de ejercicios de enlaces ionicos y covalentes"
Understanding electronegativity is essential for predicting the type of bond that will form between two atoms. This is important for understanding the properties of matter and the reactions that occur between atoms. For example, ionic bonds are typically strong and brittle, while covalent bonds are typically weaker and more flexible. This knowledge can be used to design materials with specific properties.
In summary, electronegativity is a fundamental property of atoms that influences the formation of chemical bonds. By understanding electronegativity, we can better understand the properties of matter and the reactions that occur between atoms.
Properties
The properties of ionic and covalent compounds are directly related to the strength of the bonds between the atoms. Ionic bonds are strong and brittle, while covalent bonds are weaker and more flexible. This difference in bond strength is due to the difference in the way that the electrons are shared between the atoms.
In ionic compounds, the electrons are transferred from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of positive and negative ions. The oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other by electrostatic forces, forming a strong ionic bond. The strong electrostatic forces between the ions make ionic compounds hard and brittle.
In covalent compounds, the electrons are shared between the atoms, resulting in the formation of a covalent bond. The covalent bonds between the atoms are not as strong as the ionic bonds between the ions, so covalent compounds are softer and more ductile than ionic compounds. The weaker covalent bonds between the atoms also make covalent compounds have lower melting and boiling points than ionic compounds.
The properties of ionic and covalent compounds are important for understanding the behavior of matter. For example, the hardness and brittleness of ionic compounds make them useful for making materials such as glass and ceramics. The softness and ductility of covalent compounds make them useful for making materials such as plastics and rubber.
In summary, the properties of ionic and covalent compounds are directly related to the strength of the bonds between the atoms. Ionic bonds are strong and brittle, while covalent bonds are weaker and more flexible. This difference in bond strength is due to the difference in the way that the electrons are shared between the atoms.
Examples
These examples illustrate the fundamental difference between ionic and covalent bonds. Sodium chloride is an ionic compound because it is formed between a metal (sodium) and a nonmetal (chlorine). The sodium atom transfers an electron to the chlorine atom, resulting in the formation of positive and negative ions. These ions are attracted to each other by electrostatic forces, forming an ionic bond. Water is a covalent compound because it is formed between two nonmetals (hydrogen and oxygen). The hydrogen and oxygen atoms share electrons, resulting in the formation of a covalent bond.
- Types of Bonds
Ionic and covalent bonds are the two main types of chemical bonds. Ionic bonds are formed between atoms of metals and nonmetals, while covalent bonds are formed between atoms of nonmetals.
- Properties of Compounds
Ionic compounds are typically hard, brittle, and have high melting and boiling points. Covalent compounds are typically soft, ductile, and have low melting and boiling points.
- Examples of Compounds
Sodium chloride (NaCl) is an example of an ionic compound. Water (H2O) is an example of a covalent compound.
- Importance of Understanding Bond Types
Understanding the difference between ionic and covalent bonds is important for predicting the properties of compounds and understanding chemical reactions.
By understanding the different types of bonds that can form between atoms, we can better understand the world around us. The examples of sodium chloride and water are just two of the many different types of compounds that exist, and each type of compound has its own unique properties and applications.
Importance
Ionic and covalent bonds are the two main types of chemical bonds. They determine the properties of matter by influencing the way atoms interact with each other. For example, ionic bonds are typically strong and brittle, while covalent bonds are typically weaker and more flexible. This difference in bond strength is due to the difference in the way that the electrons are shared between the atoms.
Ionic bonds are formed when one atom transfers one or more electrons to another atom. The atom that loses electrons becomes a positively charged ion, and the atom that gains electrons becomes a negatively charged ion. The oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other by electrostatic forces, forming an ionic bond. Ionic compounds are typically hard, brittle, and have high melting and boiling points. This is because the strong electrostatic forces between the ions hold the compound together tightly.
Covalent bonds are formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. The shared electrons are attracted to the nuclei of both atoms, forming a covalent bond. Covalent compounds are typically soft, ductile, and have low melting and boiling points. This is because the covalent bonds between the atoms are not as strong as the ionic bonds between the ions.
The importance of ionic and covalent bonds cannot be overstated. They determine the properties of matter and play a vital role in many chemical reactions. Understanding the difference between these two types of bonds is essential for understanding chemistry and the world around us.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section provides answers to common questions about ionic and covalent bonds.
Question 1: What is the difference between an ionic and a covalent bond?
Answer: An ionic bond is formed when one atom transfers one or more electrons to another atom. A covalent bond is formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons.
Question 2: Which type of bond is stronger, ionic or covalent?
Answer: Ionic bonds are typically stronger than covalent bonds. This is because ionic bonds are formed by the attraction between oppositely charged ions, while covalent bonds are formed by the sharing of electrons.
Question 3: What are some examples of ionic and covalent compounds?
Answer: Examples of ionic compounds include sodium chloride (NaCl) and potassium chloride (KCl). Examples of covalent compounds include water (H2O) and methane (CH4).
Question 4: What are the properties of ionic and covalent compounds?
Answer: Ionic compounds are typically hard, brittle, and have high melting and boiling points. Covalent compounds are typically soft, ductile, and have low melting and boiling points.
Question 5: Why is it important to understand ionic and covalent bonds?
Answer: Understanding ionic and covalent bonds is important because they determine the properties of matter. For example, ionic bonds are responsible for the hardness and brittleness of many materials, while covalent bonds are responsible for the softness and ductility of many other materials.
Question 6: How can I learn more about ionic and covalent bonds?
Answer: There are many resources available to learn more about ionic and covalent bonds. You can find books, articles, and videos on the topic online or at your local library. You can also take a chemistry course at your local school or university.
We hope this FAQ section has answered some of your questions about ionic and covalent bonds. If you have any further questions, please feel free to contact us.
Transition to the next article section:
In the next section, we will discuss the applications of ionic and covalent bonds in everyday life.
Conclusion
In this article, we have explored the topic of ionic and covalent bonds, providing examples and explanations of these two fundamental types of chemical bonds. We have discussed the properties of ionic and covalent compounds, and their importance in determining the behavior of matter.
Understanding ionic and covalent bonds is essential for understanding chemistry and the world around us. These bonds are responsible for the properties of all matter, from the hardness of metals to the softness of plastics. By understanding these bonds, we can better understand the materials we use every day and the reactions that occur in the world around us.
NIMS Management Characteristic: Incident Action Plan
Indulge In The Refreshing Embrace Of Water Showers: The Ultimate Guide
Why Shakespeare Is The World's Most Famous Playwright