The Core Characteristics Of Constructivism Explained
What are the characteristics of constructivism?
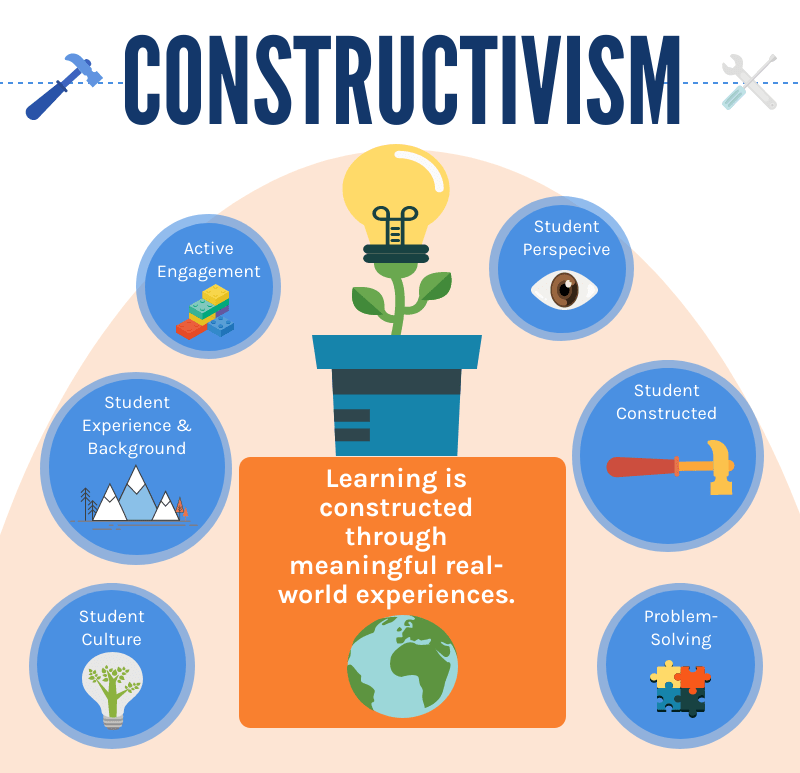
Constructivism is a theory of learning that emphasizes the role of the learner in constructing knowledge. Constructivists believe that learners actively construct new knowledge by interacting with their environment and by reflecting on their experiences. This process of knowledge construction is influenced by the learner's prior knowledge, beliefs, and experiences.
The characteristics of constructivism include:
- Learning is an active process. Learners are not passive recipients of knowledge, but rather they actively construct new knowledge by interacting with their environment and by reflecting on their experiences.
- Knowledge is constructed individually. Each learner constructs their own unique understanding of the world, based on their prior knowledge, beliefs, and experiences.
- Learning is a social process. Learners learn through their interactions with others, including teachers, peers, and family members.
- Assessment should be authentic. Assessment should be designed to measure what learners have learned, not just what they can memorize.
Constructivism has been shown to be an effective approach to learning. Studies have shown that students who learn in constructivist environments are more likely to retain information, apply their knowledge to new situations, and develop critical thinking skills.
Constructivism is an important theory of learning that has implications for teaching and learning. By understanding the characteristics of constructivism, educators can create learning environments that are more effective and engaging.
The Characteristics of Constructivism
Constructivism is a theory of learning that emphasizes the role of the learner in constructing knowledge. Constructivists believe that learners actively construct new knowledge by interacting with their environment and by reflecting on their experiences. This process of knowledge construction is influenced by the learner's prior knowledge, beliefs, and experiences.
- Active learning: Learners are not passive recipients of knowledge, but rather they actively construct new knowledge by interacting with their environment and by reflecting on their experiences.
- Individual construction: Each learner constructs their own unique understanding of the world, based on their prior knowledge, beliefs, and experiences.
- Social learning: Learners learn through their interactions with others, including teachers, peers, and family members.
- Authentic assessment: Assessment should be designed to measure what learners have learned, not just what they can memorize.
- Reflective practice: Learners should be encouraged to reflect on their learning experiences and to identify what they have learned and how they can apply it to new situations.
These five key aspects of constructivism provide a framework for understanding how learners construct knowledge. By understanding these aspects, educators can create learning environments that are more effective and engaging.
Active learning
Active learning is a key characteristic of constructivism. Constructivists believe that learners are not passive recipients of knowledge, but rather they actively construct new knowledge by interacting with their environment and by reflecting on their experiences. This process of knowledge construction is influenced by the learner's prior knowledge, beliefs, and experiences.
- Exploration: Learners actively explore their environment and seek out new experiences. They are curious and eager to learn new things.
- Experimentation: Learners experiment with new ideas and concepts. They try out different things to see what works and what doesn't.
- Reflection: Learners reflect on their experiences and what they have learned. They think about what they have done, what they have learned, and how they can apply their learning to new situations.
- Collaboration: Learners collaborate with others to learn. They share ideas, work together on projects, and help each other to understand new concepts.
Active learning is an essential part of constructivism. It allows learners to construct their own knowledge and to develop a deep understanding of the world around them.
Individual construction
Individual construction is a key characteristic of constructivism. Constructivists believe that each learner constructs their own unique understanding of the world, based on their prior knowledge, beliefs, and experiences. This process of knowledge construction is influenced by the learner's culture, social interactions, and environment.
There are a number of factors that contribute to individual construction. These include:
- Prior knowledge: Learners' prior knowledge and experiences play a significant role in how they construct new knowledge. Learners who have a strong foundation in a particular subject area are more likely to be able to learn new information in that area.
- Beliefs: Learners' beliefs about the world can also influence how they construct new knowledge. Learners who believe that they are capable of learning are more likely to be successful in their studies.
- Culture: Learners' culture can also influence how they construct new knowledge. Learners from different cultures may have different ways of thinking about the world, which can lead to different ways of learning.
- Social interactions: Learners' social interactions can also influence how they construct new knowledge. Learners who interact with others who have different perspectives are more likely to develop a more nuanced understanding of the world.
Individual construction is an important concept in constructivism. It highlights the fact that learners are not passive recipients of knowledge, but rather they actively construct their own understanding of the world. This understanding is unique to each learner and is influenced by a variety of factors. By understanding the process of individual construction, educators can create learning environments that are more effective and engaging.
Social learning
Social learning is a key characteristic of constructivism. Constructivists believe that learners learn through their interactions with others, including teachers, peers, and family members. This process of social learning is influenced by the learner's prior knowledge, beliefs, and experiences.
- Collaborative learning: Learners learn by working together on projects and assignments. They share ideas, help each other to understand new concepts, and provide feedback on each other's work.
- Peer teaching: Learners learn by teaching each other. They explain concepts to each other, answer each other's questions, and provide feedback on each other's understanding.
- Observational learning: Learners learn by observing others. They watch how others solve problems, complete tasks, and interact with the world around them.
- Modeling: Learners learn by observing the behavior of others. They imitate the behavior of others, and they adopt the values and beliefs of others.
Social learning is an important part of constructivism. It allows learners to learn from others, to develop new skills, and to gain a deeper understanding of the world around them.
Authentic assessment
Authentic assessment is a key characteristic of constructivism. Constructivists believe that assessment should be designed to measure what learners have learned, not just what they can memorize. This is because constructivism emphasizes the importance of active learning, individual construction, and social learning.
Authentic assessment tasks are designed to reflect the real-world application of knowledge and skills. They require learners to apply their learning to new situations and to solve problems. This type of assessment is more effective than traditional memorization-based assessment because it allows learners to demonstrate their understanding of the material and their ability to apply it to new situations.
There are many different types of authentic assessment tasks that can be used in the classroom. Some examples include:
- Projects: Learners work on a project that allows them to apply their learning to a real-world problem.
- Presentations: Learners present their learning to others in a way that is clear and engaging.
- Portfolios: Learners collect their work over time to demonstrate their progress and development.
- Observations: Teachers observe learners as they work on tasks and provide feedback on their progress.
Authentic assessment is an important part of constructivism. It allows learners to demonstrate their understanding of the material and their ability to apply it to new situations. By using authentic assessment tasks, educators can create learning environments that are more effective and engaging.
Reflective practice
Reflective practice is a key component of constructivism. Constructivists believe that learners should be encouraged to reflect on their learning experiences and to identify what they have learned and how they can apply it to new situations. This is because reflection is essential for deep learning. It allows learners to make connections between new and prior knowledge, to identify areas where they need additional support, and to develop strategies for applying their learning to new situations.
There are many different ways to encourage reflective practice in the classroom. Some examples include:
- Asking students to write reflective journals: Reflective journals provide students with a space to record their thoughts and feelings about their learning experiences. They can be used to track students' progress over time and to identify areas where they need additional support.
- Leading class discussions: Class discussions can be a great way to encourage students to reflect on their learning experiences and to share their insights with others. Teachers can use discussion questions to prompt students to think about what they have learned, how they have learned it, and how they can apply it to new situations.
- Providing students with feedback: Feedback can help students to identify areas where they need to improve and to develop strategies for improvement. Teachers can provide feedback on students' work, on their participation in class discussions, and on their overall progress.
Reflective practice is an essential component of constructivism. It allows learners to make connections between new and prior knowledge, to identify areas where they need additional support, and to develop strategies for applying their learning to new situations. By encouraging reflective practice, educators can create learning environments that are more effective and engaging.
FAQs on the Characteristics of Constructivism
Constructivism, a prominent theory in education, emphasizes the dynamic role of learners in constructing knowledge. This FAQ section aims to clarify common questions and misconceptions about constructivism's characteristics, providing concise and informative answers.
Question 1: What is the central principle of constructivism?
Answer: Constructivism posits that learners actively construct new knowledge through interactions with their environment and reflection on experiences, influenced by their prior knowledge and beliefs.
Question 2: How does constructivism view the role of the learner?
Answer: Constructivists see learners as active agents who engage in knowledge construction, rather than passive recipients of information transmitted by an instructor.
Question 3: What is the significance of social interaction in constructivism?
Answer: Constructivism recognizes the importance of social learning, as individuals construct knowledge through interactions with peers, teachers, and the broader community.
Question 4: How does constructivism influence assessment practices?
Answer: Constructivist assessment focuses on authentic tasks that allow learners to demonstrate their understanding and ability to apply knowledge in meaningful contexts.
Question 5: What is the role of reflection in constructivist learning?
Answer: Reflection is crucial for constructivism, as it enables learners to critically examine their learning experiences, identify areas for growth, and refine their understanding.
Question 6: How can educators effectively implement constructivist principles in their teaching?
Answer: To implement constructivism, educators can encourage active learning, provide opportunities for collaboration, incorporate authentic assessment, and foster a classroom environment that supports learner reflection.
Summary: In summary, constructivism's characteristics emphasize the active role of learners in constructing knowledge through interactions, social learning, authentic assessment, and reflective practice. By understanding these principles, educators can create learning environments that empower learners to become active and engaged constructors of their own understanding.
Transition: This FAQ section has provided a concise overview of the characteristics of constructivism. For further exploration of this topic, please refer to the comprehensive article on constructivism.
Conclusion
Constructivism's emphasis on active learning, social interaction, authentic assessment, and reflective practice provides a framework for educators to create learning environments that foster deep understanding and critical thinking. By understanding the characteristics of constructivism, educators can empower learners to become active agents in their own learning journey.
As educational practices continue to evolve, constructivism remains a cornerstone of progressive teaching methodologies. Its focus on the learner's role in knowledge construction aligns with the growing recognition of the importance of student-centered and experiential learning. Embracing constructivist principles can transform classrooms into vibrant and engaging spaces where learners are motivated to explore, collaborate, and construct meaningful knowledge.
Unlock Your Productivity: Access Office 365 Desktop Apps Anytime, Anywhere
Optimal Executor Configuration For Spark: Unlocking Peak Performance
Ultimate Guide To Open Vowel Words: Definition, Rules, And Examples